Spiritual Scientific Notes on Goethe's Faust, Vol. II
GA 273
4. Faust and the “Mothers”
2 November 1917, Dornach
My dear friends,
What I am going to speak about this evening I should like to link on to the scenes we have just witnessed. And what can be said in this regard will fit in well with the whole course of our present considerations.
Now I have often spoken here before about the importance of the ‘Mothers scene’ in the second part of Goethe's “Faust”; this scene, however, is of such a nature that one can repeatedly return to it because through its significant content, apart from the aesthetic value of the way in which it is introduced into the poem, it really contains a kind of culminating point of all that is spiritual in present day life. And if this ‘Mothers scene’ is allowed to work upon us, we shall well be able to say that it contains a very great deal of all that Goethe is wishing to indicate. It comes indeed out of Goethe's immediate soul experiences just as on the other it throws light on the significant, deep knowledge that we are obliged to recognise in him if we are to have any notion at all of what is meant by this scene where Faust is offered by Mephistopeles the possibility of descending to the Mothers. If we notice how, on Faust's reappearing and coming forth from the Mothers, the Astrologer refers to him as ‘priest’, and that Faust henceforward refers to himself as ‘priest’, we have to realise that there is something of deep import in this conversion of what Faust has been before into the priest. He has descended to the Mothers: he has gone through some kind of transformation. Leaving aside what one otherwise knows of the matter and what has been said by us in the course of years, we need reflect only upon how the Greek poets, in speaking of the Mysteries, refer to those who were initiated as having learnt to know the three world-Mothers—Rhea, Demeter and Proserpina. These three Mothers, their being, what they essentially are—all this was said to be learnt through direct perception by those initiated into the Mysteries in Greece.
When we dwell upon the significant manner in which Goethe speaks in this scene, and also upon what takes place in the next, we shall no longer be in any doubt that in reality Faust has been led into regions, into kingdoms, that Goethe thought to be like that kingdom of the Mothers into which the initiate into the Greek Mysteries was led. By this we are shown how full of import Goethe's meaning is.
And now remind yourselves of how the moment Mephistopheles mentions the word ‘Mothers’ Faust shudders, saying what is so full of meaning: “Mothers, Mothers! How strange that sounds!” And this is all introduced by Mephistopheles' words “It is with reluctance that I disclose the higher mystery.” Thus it is really a matter here of something hidden, a mystery, that Goethe, in this half secret way, found necessary to impart to the world in connection with the development of his Faust.
We must now ask, and are able to do so on the basis of what we have been considering during these past years, what is supposed to happen to Faust in the moment that this higher mystery is unveiled before him? Into what world is he led? The world, into which he is led, the world he now enters, is the spiritual world immediately bordering on our physical one.
Please remember clearly how I have already said that the crossing of the threshold into this world beyond the border must be approached in thought with great caution. As I said, this is because between the world that we observe with our senses and understand with our intellect, and that world from which the -physical one arises, there is a borderland as it were, a sphere where one may easily fall into deception and illusion when not sufficiently developed and prepared. It might be said that only in the world comprehended by the senses are there definite forms, definite outlines and boundaries. These do not exist in the world that is on other side of the border. This is something that it is very difficult to get the modern materialistic intellect to grasp—that in the moment that the threshold is passed everything is in constant movement, and the world of the senses rises out of all this continual movement like petrified forms.
It is into this world so penetrated by movement—the imaginative world—that Faust is now transplanted; transplanted, however, by an external cause end not by gradual painstaking meditation. The cause comes from without. It is Mephistopheles, the force of evil working into the physical, who takes him over to the other world.
And now there is something to which we must be very much alive to if we are not to develop errornous opinions in this sphere. We, in anthroposophical circles, are seeking knowledge of the spiritual world. And everything said in the book “Knowledge of the Higher Worlds,” and other books of that nature, about the exercises for gaining admittance into those worlds, goes no farther than the means by which this knowledge may be obtained. And here, as far as the present time and necessity are concerned in the giving out of these things to the world, it goes without saying that a halt must be made. Anyone wishing to advance beyond this, will come to the sphere that can be called the sphere of action in the supersensible world. This must be left to each individual. When he has once found the security of knowledge, he himself must undertake the action. But in what is meant to proceed between Faust and Mephistopheles this is not the case. Faust has actually to produce the departed Paris and Helen; therefore he does not only have to look into the spiritual world, he does not have to be an initiate only, but a magician, and must accomplish magical actions. It very clearly shown here in the way this scene is handled by Goethe how deeply familiar he was with certain hidden things in the human soul. The state of Faust's consciousness has to be changed. But at the same time he has to be given power to act out of supersensible impulses.
In his connection with Faust, Mephistopheles, in his capacity as an ahrimanic force, belongs to our world of the senses, but as a supersensible being. He has been transplanted. He has no power over the worlds into which Faust is now to be transplanted. They really do not exist for him. Faust has to pass over into a different state of consciousness that perceives, beneath the foundation of our world of the senses, the never-ceasing weaving and living, surging and becoming, from which our sense-world is drawn. And Faust is to become acquainted with the forces that are there below.
The ‘Mothers’ is a name not without significance for entering this world. Think of the connection of the word ‘Mothers’ with everything that is growing, becoming. In the attributes of the mother is the union of what is physical and material with what is not. Picture to yourselves the coming into physical existence of the human creature, his incarnation. You must picture a certain process that takes place through the interworking of the cosmos with the mother-principle, before the union of the male and female is consummated. The man who is about to become physical prepares himself beforehand in the female element. And we must now make a picture of this preparation that is confined to what goes on up to the moment when impregnation takes place—all therefore that takes place before impregnation. One has a quite wrong and materialistically biased notion if one imagines that there lie already formed in the woman all the forces that lead to the physical human embryo. That is not so. A working of the cosmic forces of the spheres takes place; into the woman work cosmic forces. The human embryo is always a result of cosmic activity. What is described in materialistic natural science as the germ-cell is in a certain measure produced out of the mother alone, but it is a counterpart of the great cosmic germ-cell.
Let us hold this picture in mind—this becoming of the human germ-cell before impregnation, and let us ask ourselves what the Greeks looked for in their three mothers, Rhea, Demeter and Proserpina. In these three Mothers they saw a picture of those forces that, working down out of the cosmos, prepare the human cell. These forces however do not come from the part of the cosmos that belongs to the physical but to the supersensible. The Mothers Demeter, Rhea and Proserpina belong to the supersensible world. No wonder then that Faust has the feeling that an unknown kingdom is making its presence felt when the word ‘Mothers’ is spoken.
Now think, my dear friends, what Faust really has to experience. If it were purely a matter of imaginative knowledge he would only need to be led into the normal state of meditation but, as has been said, he has to accomplish magical actions. For that it is necessary that the ordinary understanding, the ordinary intellect, with which men perceives the world of the senses, should cease to function. This intellect begins with incarnation into a physical body and ends with physical death. And it is this intellect in Faust that must be damped-down, clouded. He has to recognise that his intellect should cease to work. He must be taken up with his soul into a different region. This naturally should be understood as a significant factor in Faust is development.
Now how does the matter appear from Mephistopheles' point of view? We must understand that there is danger in the fact that it is Mephistopheles who has to transform Faust's state of consciousness. And it gives the former himself a sense of uneasiness; in a certain way it becomes dangerous for him also. What then are the possibilities? They are twofold. Faust may acquire the new state of consciousness, learn to know the other world from which he can draw upon miraculous forces, and go to and fro from one world to the other, thus emancipating himself from Mephistopheles for he would then learn to know a world where the latter had no place. With that he would, become free from Mephistopheles. The other possibility would be that all might go very badly and Faust's intellect become clouded. Mephistopheles really puts himself in a very awkward situation. However, he has to do something. He has to give Faust the possibility of fulfilling his promise. He hopes that in some way or another the matter may arrange itself, for he wants neither of the alternatives. He does not want Faust to grow away from him nor does he wish him to be completely paralysed.
I ask you to think over this and then to remember that it is all this that Goethe wants to indicate. In this scene of Faust he wishes to point out to the world that there is a spiritual kingdom, and that here he is showing the way in which man can relate himself to it. This is how things are connected.
Since the beginning of the fifth post-Atlantean epoch the knowledge of these things has to a great extent been lost. I have told you that Goethe applied the knowledge he had personally received through great spiritual vision. The whole connection with the Mothers had entered into Goethe's soul when he read Plutarch. For Plutarch, the Roman story-teller whom Goethe read, speaks of the Mothers; and the following particular scene in Plutarch seems to have made a deep impression on Goethe. The Romans were at war with Carthage. Nicias is in favour of the Romans and wishes to seize the town of Engyon from the Carthaginians; he is therefore to be given over to the Carthaginians. So he feigns madness and runs through the streets crying “The Mothers—the Mothers are pursuing me!” From this you may see that in the time of which Plutarch writes this relation of the Mothers is brought into connection not with the normal understanding of the senses, but with a condition of man when this normal understanding is not present. It is beyond all doubt that what Goethe read in Plutarch stirred him to bring to expression in his “Faust” this idea of the Mothers.
We also find mention in Plutarch of how the world has a triangular form. Now naturally these words ‘the world has a triangular form’ must not be taken in a heavy literal sense, for the spatial is but a symbol of what has neither time nor space. Since we live in space, spatial images must be used for what is nevertheless beyond image, time or space.
Thus Plutarch gives the picture of a triangular world. This the whole world (see diagram). According to Plutarch in the centre of this triangle that is the world, the field of truth is found. Now out of this whole world Plutarch differentiates 183 worlds. 183 worlds, so he says, are in the whole circumference; they move around, and in the middle is this resting field of truth. This resting field of truth Plutarch describes as being separated by time from the surrounding 183 worlds—sixty on each of the three sides of the triangle and one at each angle makes 183. When, therefore, you take this imagination of Plutarch's, you have a world considered as consisting of three parts and in the cloud formation around it the 183 worlds welling and surging. That is at the same time the imagination for the “Mothers.” The number 183 is given by Plutarch.
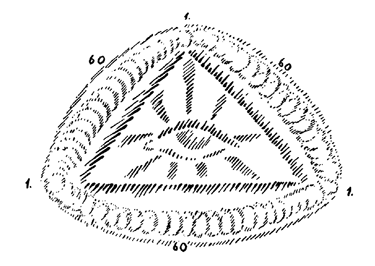
Thus Plutarch, who in a certain sense held sway over the mystery wisdom, quoted the remarkable number 183. Let us now reckon how many worlds we get if we make a correct calculation up to the time of Plutarch's world. We must do so in the following way:
| First the entire world happenings | 1 |
| This divides itself up for us so that we have as complete world-evolutions Saturn, Sun and Moon | 3 |
But each of these worlds, Saturn, Sun and Moon, are again divided in the same way as our Earth. We divide our Earth into: The Polaric Period, And each of these seven periods [ages] we again divide into the seven epochs. Our present, the first post Post-Atlantean Period is divided into: Indian, the old Persian, the Egyptian, the Greco-Latin, the present epoch and two to follow. If we take this for Saturn, Sun and Moon, we have the successive worlds built up in the following way: 3 times 7 periods x 7 epochs (49 epochs) |
49 49 49 |
After these three successive worlds we still have to add the Earth that has not yet completed its development. The Polaric 7, Hyperborean 7, Lemurian 7(21), the Atlantean 7 |
28 | = |
| 179 | |
We have now completed Atlantis. Plutarch lived in the fourth epoch, of Post-Atlantis, so we must add |
4 |
| = | |
| The number of epochs of the world evolution | 183 |
You see how when we apply our own way of reckoning and correctly calculate the separate divisions and the whole world, as they have made their evolutions up to the time of the fourth Post-Atlantean epoch when Plutarch lived, we can truthfully say that we get 183 worlds.
Moreover, when we take our Earth upon which we are still evolving, and about which we cannot speak as of something completed, and when we look from this Earth to Saturn, Sun and Moon, there we find the “Mothers” that figure in another form in the Greek Mysteries under names Proserpina, Demeter and Rhea. For all the forces that are in Saturn, Sun and Moon are still working—working on into our own time. And those forces that are physical are but the shadow, the image, of what is spiritual. Everything physical is a mere picture of the spiritual.
Consider this. If you do not take simply its outward, gross physical body, but its forces, its impulses, the Moon with its forces is at the same time in the Earth. The being of the Moon belongs to the being of the Earth. If you only want a realistic picture, you need to imagine it thus. Here is the Earth (see diagram); here you have a shaft connected with the Moon, and the Moon is turned round on it The shaft, however, has no physical existence. And all that is Moon-impulse is not only here in the Moon but this sphere penetrates the Earth.

We now ask whether these forces thus related to the Moon have a real existence anywhere. The Greeks looked upon them as mysterious, as very full of mystery. And our modern destiny is connected with the fact that these forces no longer retain their character as mysteries but have been made available for all. If we only concentrate on this one thing, on these forces that are connected with the Moon—then we have one of the Mothers. What is this one Mother? We shall best approach the answer to this question in the following way.
In order to have a picture let us take any river—say the Rhine. What is the actual Rhine? On reflection—I have already spoken of this here—no one is really able to say what the Rhine is. It is called the Rhine. But what actually is it when we look into the matter? Is it the water? But in the next moment that has flowed away water has water has taken its place. It flows into the North Sea and other water and follows it, and that goes on continuously. Then what is the Rhine? Is the Rhine the trough, the bed? But no one believes that, for were the water not there no one would think of the bed as the Rhine. When you use the word ‘Rhine’ you are not referring to anything really there but to something in a constant state of metamorphosis—which, however, in certain sense does not change. If we picture this diagrammatically (see diagram) and assume that this is the Rhine and this the water that flows into it—well, now, this water is always evaporating and descending again.

If you consider that all rivers belong to one another, you will have to take into your calculations that the water evaporates and then falls again. To a certain extent the water that flows from its source down to its mouth always comes over again from the same reservoir in its rising and flowing down. The water completes its circulation here. But this water is divided up an extended over the surroundings; naturally you cannot follow the course of each drop. All the water that belongs to the earth, however, must be considered as a whole. The question of rejuvenating water does not come into consideration here, This is what happens where the water is concerned.
Something the same happens with the air, and in yet another case. If you have a telegraph station here and here another, you know that it is only a wire that connects them. The other connection is set up by means of the whole earth, the current goes down into the earth. Here is the place where it is earthed. The whole goes through the earth.
Now if you make a picture of these two things you have the water, the running water that spreads itself out and sets itself in circulation; and if on the other hand you imagine the electricity spreading itself out down in the earth, then you have two things at different poles—two opposed realities. I am only indicating here, for you can piece it together yourselves out of any elementary book on physics. But we are led to the conclusion that in electricity you have under the earth the opposite of what goes on above the earth in the circulation of the water.
What is there under the earth ruling as the being of electricity is Moon-impulse that has been left behind. It definitely does not belong to the earth. It is impulse remaining over from the Moon and was spoken of as such by the Greeks. And the Greeks still had knowledge of the relation between this force, distributed throughout the whole earth, and the reproductive forces. And there is this relation with the forces of growth and of increase. This was one of the ‘Mothers.’
Now you can imagine that all these premonitions of mighty connections did not arise before Faust merely as theories, but he felt himself obliged to seek out—to enter right into these impulses. Knowledge of this force was first of all given to those being initiated into the Greek Mysteries, this force together with the two other Mothers. The Greeks held all that was connected with electricity in secret in the Mysteries. And herein is where lies the decadence of the future of the earth—of which I have already spoken from another point of view—that these forces will be made public. One of these forces has already become so during the fifth post-Atlantean epoch—electricity. The others will be known about in the decadence of the sixth and seventh epochs.
All this, even in the decadent new secret societies, is still among the things about which their conservative members will not speak. Goethe quite rightly judged it fit to give out knowledge of these things in the only way possible for him in that age. At the same time, however, you have one of the passages from which you can see how the great poet Goethe did not simply write as other poets write, but that each word of his bore its special impress and had its appointed place.
Take for example the relation of the Mothers to electricity. Goethe belongs to those who treat of such things out of a thoroughly expert knowledge.
“Do you now see what one possesses in it?
The key will ferret out the proper place.
Follow it up, it leads you to the Mothers.”
And Faust:
“To the ‘Mothers’. That strikes me always like a shock!”
as if he had received an electric shock. This is written with intention—not haphazardly. In this scene nothing in connection with the matter in question is haphazard.
Mephistopheles gives Faust a picture of what he is to find as the impulses of the 183 worlds. This picture works in Faust's soul as it should work, for Faust has gone through many things that bring him near the spiritual worlds. On that account these things already affect him.
This is what I wanted chiefly to dwell upon, my dear friends, hew Goethe is wishing to set forth the most significant matters in this 'Mothers' scene. And by all this you can see from what worlds—what worlds of different consciousness—Faust has to bring Paris and Helen. Because Goethe is dealing with something of such supreme significance, what is spoken in this scene is actually different from what it appears at first sight. What Faust brings with him from these worlds—what I have already referred to—is recognised by the others who have assembled for a kind of drama. What makes them see it? It is half suggested: but by whom? By the Astrologer; and for that he has been chosen as astrologer. His words possess suggestive power. This is clearly expressed. These astrologers had an inherent art of influencing through suggestion, not the best kind of suggestion but an ahrimanic one. What then is our Astrologer actually doing as he stands among these courtiers, who really are not pictured as being particularly bright,—what is he doing? He is putting into them by suggestion what is necessary for all that has arisen as a special world through Faust's changed consciousness to become present in their minds. Remember what I showed you, what I once said to you, that nowadays it can be actually proved that spoken words produce a trembling in certain substances. You will surely find it in one or another of the lectures I have previously given here. I have wanted to remark upon this to show you how today the real nature of the conjuration scene can be demonstrated by experiment. Out of the smoke of the incense and the appropriate accompanying word is really developed what Faust brings for his consciousness out of quite another world. But this must be brought to the minds of the courtiers and made fully clear to them through the suggestive power of the Astrologer. What then does he do? He insinuates. He has the task of insinuating all this into the courtiers' ears. But insinuation is devil's rhetoric. So that through the words ‘insinuation is devil's rhetoric’ the devilish nature of the astrologer's art is brought home to us. That is the one meaning of the sentence. The other is connected with what actually happens on the stage. The devil sits in the prompter's box making his insinuations from there.
Here you have a very prototype of a sentence signifying two different things. You have the purely scenic significance of the devil himself sitting, insinuation from the prompter's box, and the reality of this—the Astrologer insinuating to the Court. In the way he does this it is a devilish art. Thus, if you go to work in the right way, you will find many sentences here with double meaning. Goethe employs this ambiguity because he wishes to represent something that actually happened but did not do so purely in a course-grained, material fashion. It can be performed thus, but its reality has nothing to do with the physical. Goethe, however, wanted to portray something that actually happened and was moreover an impulse in modern history and played a part there. He did not intend that something of this kind was simply to be performed, he meant to show that these impulses had already flowed into modern history, were already there, were working. He wanted to represent a reality, and to say that, in what has been developing since the sixteenth century, the devil has definitely played a part. If you take this scene seriously you will got the two sides of the matter, and you will realise how Goethe knew that spiritual beings were playing into historic processes. And at the end you come to what I have so often indicated, namely, that Faust is not yet sufficiently developed to bring the matter to a conclusion, that he has not derived the possibility of entering other worlds from the right source but from the power of Mephistopheles. All this is what forms the last part of the scene.
I shall add more to this tomorrow and bring our considerations further. But you have seen enough to know that in what Goethe wishes to say much of what we have been studying lately receives new light.

